Bleeding Gums: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
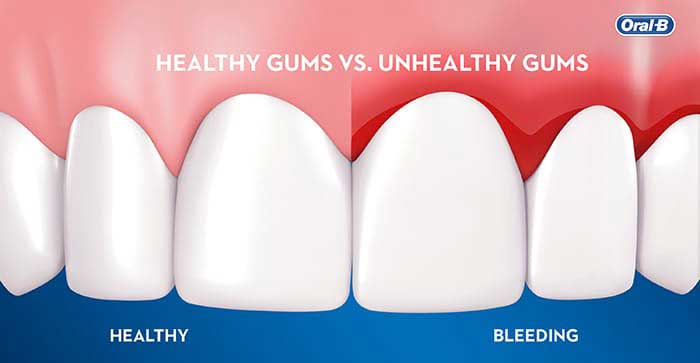
Summary
We'll discuss the available treatment and prevention options, so you know what to do to remedy the situation and keep it from happening again.
Key Takeaways
- Takeaway #1: Bleeding gums can be caused by several different factors, including trauma to your gums, aggressive brushing and flossing, long-term plaque and tartar buildup, gum disease, hormonal changes, health conditions, certain medications (e.g., blood thinners), and vitamin deficiencies.
- Takeaway #2: Bleeding gums are usually accompanied by other symptoms, such as bad breath, loose teeth, receding gums, bleeding when you brush or floss, and red, swollen, or tender gums.
- Takeaway #3: To treat bleeding gums caused by gum disease, your dentist may recommend professional cleanings, scaling and root planing (a deep cleaning). In more advanced cases where other issues have developed, treatments like fillings, a root canal, or tooth removal may be necessary.
- Takeaway #4: Bleeding gums can be prevented by maintaining a good oral hygiene routine, visiting the dentist for a cleaning as recommended, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding tobacco use.
Table of Contents

This blog has been reviewed and approved by Dr Robert Lee, a dental professional of 35 years
LEARN MORE >Key Takeaways
Causes of Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums can occur because of various factors, ranging from a one-time injury that will heal itself to a major dental or medical problem that requires professional help.
Trauma to Your Gums
One of the most common causes of localized gum bleeding is a crunchy or hard piece of food that pokes or cuts the soft tissue around your teeth. This type of trauma will often heal itself and is usually not a cause for concern.
If, however, the bleeding won't stop and is long term, there may be something caught in the wound that is keeping your body from healing. Visit your dentist right away for professional help.
Aggressive Brushing and Flossing
Aggressive brushing and flossing can cause your gums to bleed. Usually, this is a result of using a toothbrush with hard bristles aggressively, using too much force while you brush, or putting a lot of pressure on your gums when you floss.
Plaque and Tartar Buildup
Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth and gums. If it’s not removed regularly through brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar (also called calculus) in as little as 24 to 48 hours. This tartar buildup irritates your gums and can cause them to bleed.
Keep in mind that plaque is the beginning stage of tartar (and a lot of other dental issues); it can be prevented with a good oral hygiene routine that includes effective brushing, flossing, and rinsing with an antibacterial mouthwash.
Tartar, on the other hand, cannot be treated at home and requires a dental professional with special tools and training to remove it.
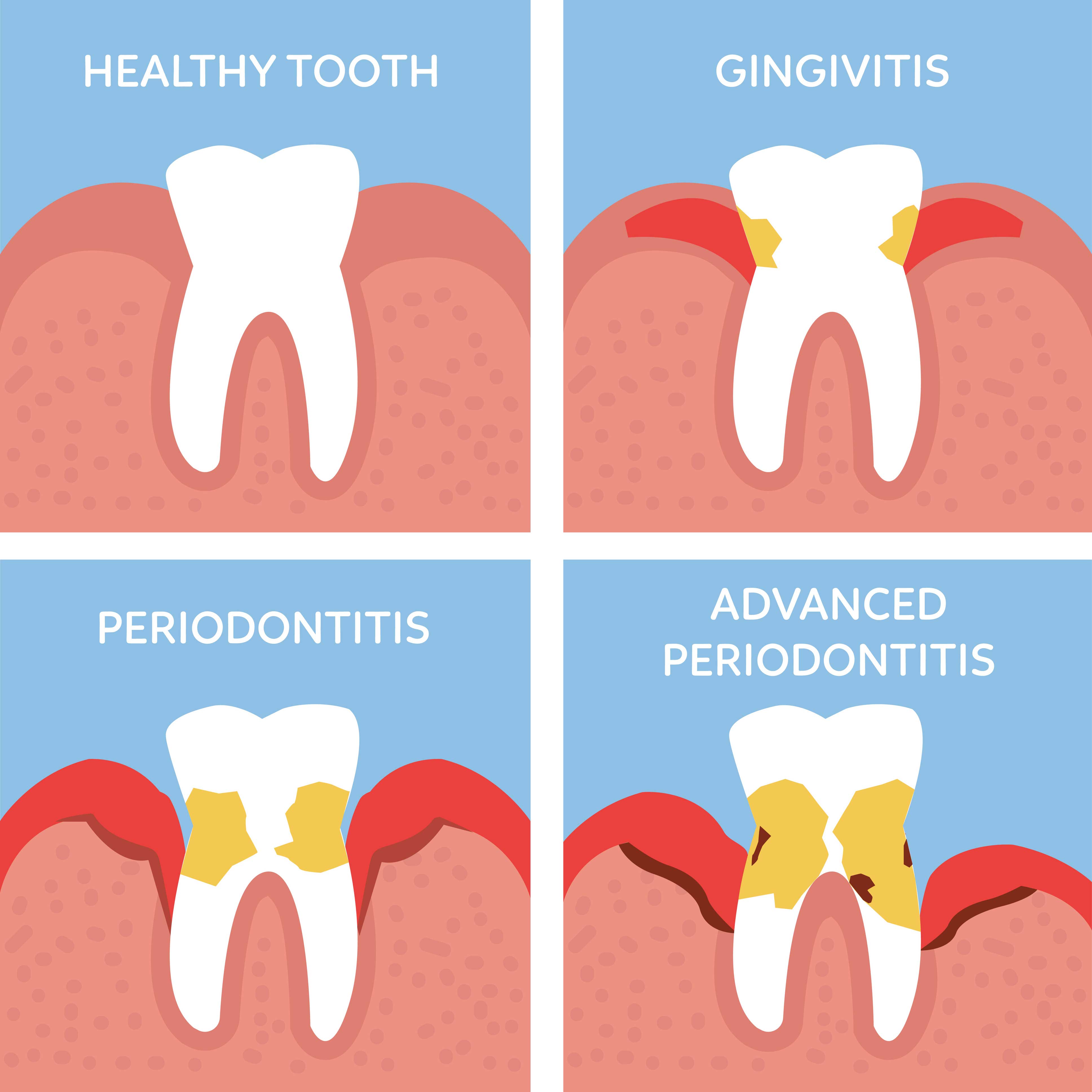
Gingivitis and Periodontitis
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease and is characterized by red, inflamed gums that may bleed from time to time.
Periodontitis is a more advanced gum disease that can result in irreversible damage to the tissue that supports your teeth and the bone underneath.
Medical Conditions
Bleeding gums can be a sign of an underlying medical condition in your body, such as:
- Diabetes
- Leukemia
- Hemophilia
- Pernicious anemia
- HIV/AIDS
- Thrombocytopenia
If your gums bleed regularly no matter what you do, visit a dentist or a general practitioner right away for a more thorough diagnosis.
Blood Thinners
Depending on your age and other medical conditions, your bleeding gums may be caused by blood thinners.
Blood thinners are necessary medications for many conditions and should not be stopped without a doctor's guidance.
Keep in mind that some blood thinners are prescribed to be taken long-term, while others are prescribed for a few weeks only.
If you're on blood thinners of any kind, use a toothbrush with very soft bristles and soft floss to reduce any discomfort associated with oral care and to reduce your risk of bleeding gums.
Brush and floss gently; don't apply too much pressure. Be sure to wear a mouthguard if you participate in a contact sport because blood thinners will make you more susceptible to bleeding in the event of a mouth injury.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes are another common cause of bleeding gums. Females are more susceptible to these changes as they go through puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, but males can also experience hormone changes that can result in bleeding gums.
Vitamin Deficiencies
If you're not getting enough of certain vitamins in your diet, your gums may start to bleed. The two most common vitamin deficiencies involve vitamin K and vitamin C.
If you think a vitamin deficiency may be the cause of your bleeding gums, add these foods (among others) to your diet:
- Spinach (Vitamin K)
- Kale (Vitamin K)
- Collard greens (Vitamin K)
- Broccoli (Vitamin K)
- Brussels sprouts (Vitamin K)
- Eggs (Vitamin K)
- Cheese (Vitamin K)
- Oranges (Vitamin C)
- Lemons (Vitamin C)
- Limes (Vitamin C)
- Guava (Vitamin C)
- Papaya (Vitamin C)
- Kiwi (Vitamin C)
- Raspberries (Vitamin C)
- Blueberries (Vitamin C)
Symptoms That May Accompany Bleeding Gums
There are a number of symptoms that can occur before your gums start to bleed and even stick around after you notice the problem. Here are some of the most common signs that there may be something else going on in your mouth.
Bleeding When You Brush or Floss
One of the first symptoms you may notice is slight bleeding when you brush or floss—especially if you're too aggressive with either.
Red, Swollen, or Tender Gums
Your gums may start to feel tender, become swollen, and change color from their normal pink to a deep shade of red.
Bad Breath
If the issue causing your bleeding gums goes untreated, you may develop persistent bad breath. This is often caused by the buildup of plaque bacteria and food debris in your mouth.
Loose Teeth
Advanced oral problems can result in loose teeth if left to progress for too long.
Receding Gums
At some point, your gums may start to recede (pull away from your teeth) and expose surfaces at and below the gum line where plaque, and tartar can accumulate to cause additional problems.
Treatment for Bleeding Gums
If your gums are bleeding often, visit your dentist to determine the underlying cause. The treatment they recommend depends on the diagnosis, but they may suggest improving your oral hygiene routine, using an antibacterial mouthwash, or having a professional cleaning.
If bleeding gums are a result of advanced gum disease or related complications, your dentist may need to address those issues with treatments such as:
- Fillings: to fix cavities where bacteria can gather.
- Root canal: to save a tooth that has become infected.
- Tooth extraction: as a last resort for a tooth that cannot be saved.
If your bleeding gums are a symptom of an underlying medical condition, a general practitioner or a specialist will have to treat the underlying condition.
With these treatment options in mind, let's take a look at how to prevent bleeding gums in the first place.
How to Prevent Bleeding Gums
Maintain a Good Oral Hygiene Routine
One of the best ways to prevent bleeding gums is to maintain a good oral hygiene routine. This includes brushing twice a day with a stannous fluoride toothpaste like Crest Pro-Health Advanced Gum Restore, flossing once a day, and swishing with an antigingivitis/antibacterial rinse like Crest Pro-Health Gum Care Mouthwash.
Get a Professional Cleaning Twice a Year
Despite your best efforts, some plaque will remain on your teeth. . That's why it's important to visit your dental professional for regular cleanings as often as they recommend, which is typically every six months.
With their training and special tools, your dental professional will be able to remove the tartar and help you learn how to prevent plaque buildup that can lead to bleeding gums.
Eat a Healthy Diet
The foods you eat every day play a big role in your oral (and overall) health. Build your diet around lean proteins and lots of fruits and vegetables. This will give your body the fuel it needs to stay as healthy as possible.
Avoid Smoking and Chewing Tobacco
Tobacco reduces blood flow to your gums, slows down tissue repair, and prevents your body from fighting off infection, all of which make it much more difficult to prevent bleeding gums and other dental issues.
Quit smoking to give your teeth and gums the best chance to be healthy. If you're having trouble quitting, talk to your dentist or primary care physician for advice and support.
A Healthy Mouth Starts with Oral-B

When you suffer from bleeding gums, an effective yet gentle oral hygiene routine is essential for healing.
We recommend brushing with an advanced electric toothbrush like the Oral-B iO9 Electric Toothbrush. Its dentist-inspired round brush head combines powerful, yet gentle, micro-vibrations with oscillating-rotating action for a professional clean feeling every day. For an even gentler experience, pair it with an Oral-B iO Gentle Care Replacement Brush Head. The built-in Smart Pressure Sensor is also key—it turns red when you’re brushing too hard, helping protect your gums from excess pressure.
FAQs
-
Why do my gums bleed when I floss?
-
Is bleeding gums always a sign of gingivitis?
-
Can using a hard-bristled toothbrush cause bleeding gums?
-
How can I treat bleeding gums at home?
-
Why do gums bleed during pregnancy?
Sources
- https://crest.com/en-us/oral-care-tips/gum-health/bleeding-gums-causes-treatments-prevention?srsltid=AfmBOoqbT76tslyChKg18pyuawR-WXh9-PInkjubAzMt5Dq74cXY6mSa
- https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/gum-disease
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/ 24908-bleeding-gums
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/ 003062.htm
- Biesbrock, A., et al. (2019). The effects of bioavailable gluconate chelated stannous fluoride dentifrice on gingival bleeding: Meta-analysis of eighteen randomized controlled trials. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 46(12), 1205-1216. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13203
- Geurs, N. C., et al. (2023). A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial of Prenatal Oral Hygiene Education in Pregnancy-Associated Gingivitis. Journal of Midwifery & Women's Health, 68(4), 507-516. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmwh.13486
- Grender, J., et al. (2022). A 12-Week Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing a Novel Electric Toothbrush With an Extra Gentle Brush Head to a Manual Toothbrush for Plaque and Gingivitis Reduction. Compendium of Continuing Education in Dentistry (Jamesburg)
- Zou, Y., et al. (2024). A meta-analysis comparing toothbrush technologies on gingivitis and plaque. International Dental Journal, 74(1), 146-156.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.identj.2023.06.009
Table of Contents
- Causes of Bleeding Gums
- Symptoms That May Accompany Bleeding Gums
- Treatment for Bleeding Gums
- How to Prevent Bleeding Gums
- A Healthy Mouth Starts with Oral-B
-
- FAQs
- Sources

This blog has been reviewed and approved by Dr Robert Lee, a dental professional of 35 years
LEARN MORE >
Sign Up
for gum care tips, expert advice, and exclusive offers.

Sign Up
for gum care tips, expert advice, and exclusive offers.




