Receding Gums: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Summary
In this article, you’ll learn about the causes and symptoms of receding gums, as well as how to treat and prevent gum recession and get back to a healthier smile.
Key Takeaways
- Takeaway #1: Receding gums is a condition that occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back from the teeth.
- Takeaway #2: Causes of receding gums include periodontal disease, genetics, brushing too hard, poor dental care, hormone levels, using tobacco products, grinding or clenching your teeth, and a crooked or misaligned bite.
- Takeaway #3: Symptoms you may notice along with gum recession include long teeth, exposed roots, and loose teeth.
- Takeaway #4: Mild gum recession can often be managed by treating the underlying cause, such as with a professional deep cleaning for any associated gum disease. More severe receding gums may require surgery.
- Takeaway #5: To prevent receding gums, follow a good oral hygiene routine that includes brushing at least twice a day and flossing once a day, quit using tobacco products, eat a healthy diet, and visit your dental professional at least two times a year for professional cleanings and check-ups.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
What Are Receding Gums?
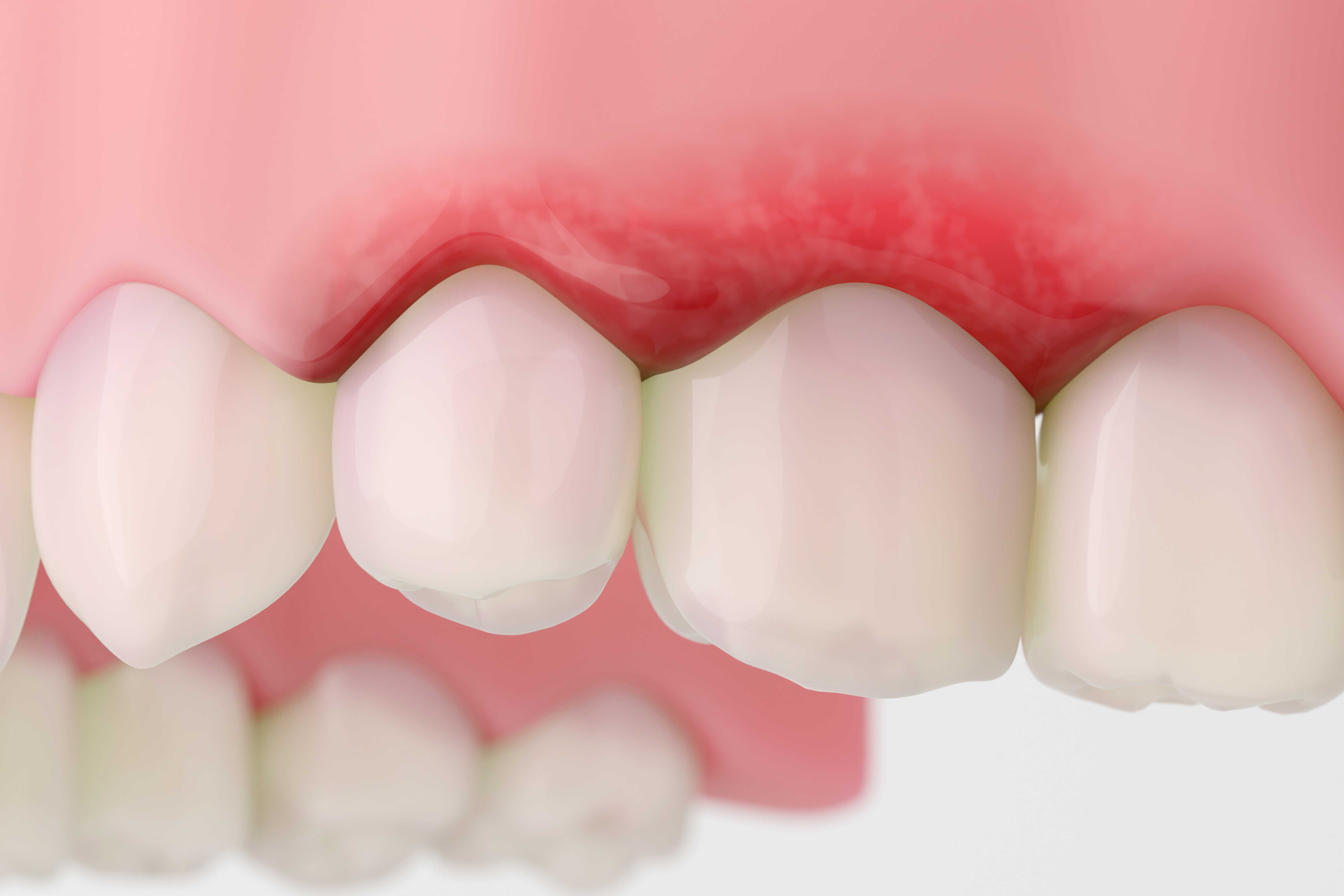
Receding gums, or gum recession, is a condition that occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away, or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or the tooth's root.
When gums recede, pockets can form between the gum and tooth, allowing disease-causing bacteria to build up. If left untreated, the bacteria can damage surrounding tissue and bone structures of the teeth, sometimes resulting in tooth loss.
Receding gums is a widespread dental condition that progresses gradually.
Receding Gums vs. Normal Gums
Trying to figure out if you have receding gums can be tricky — especially in the early stages. Here’s a quick comparison of receding gums vs. normal gums to help you recognize potential signs.
Normal gums:
- Are typically pink in color
- Fit snugly around your teeth
- Are more or less consistent and even from one side of your jaw to the other
- Cover the root of your teeth
Receding Gums:
- Appear red (or otherwise discolored)
- Are sometimes inflamed
- Appear to be pulling away from your teeth, causing the teeth to look longer than usual
- Create a noticeable “notch” or indentation where the gum meets the tooth
- Are uneven from one side of your jaw to the other
- Have receded enough to reveal the root of the tooth
Receding gums can take years to develop or become apparent in a matter of weeks. Regardless, visit your dentist right away to keep the issue from becoming a bigger problem.
Causes of Receding Gums
Numerous factors can cause gum recession, including:
Periodontal Diseases
These are gum infections, caused by bacteria, that destroy gum tissue and the bone that holds your teeth in place. Periodontitis, the more advanced form of gum disease, is a primary cause of gum recession.
The early stage of gum disease is often not painful; therefore, symptoms often go unnoticed. Left untreated, though, early symptoms can develop into periodontitis — a serious gum tissue infection.
Early stages of gum disease can be seen with minor symptoms, including:
- Red, swollen, or purple gums
- Gums that feel tender to the touch
- Bleeding gums
- Chronic bad breath
Genetics
Some people are more susceptible to periodontal disease than others. Studies show that 30% of the population may be predisposed to gum disease, even if they take good care of their teeth.
Brushing Too Hard
Brushing your teeth too aggressively or with improper technique can cause the gum tissue to wear away, leading to gum recession. Once the gums have receded, the tooth’s root surface (cementum) is exposed, and abrasive brushing can then wear away this surface and the enamel.
Poor Dental Care
Inadequate brushing, flossing, and rinsing can make it easy for plaque to turn into tartar, a hard substance that forms on and between your teeth. Tartar can only be removed by a professional dental cleaning.
If tartar has built up below the gumline and caused gum disease, your dental professional may perform scaling and root planing — a procedure that removes tartar from both above and below the gum line. This is different from a standard professional cleaning.
Hormone Levels
Changes in estrogen levels over a woman's life — such as during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause — can make gums increasingly sensitive and vulnerable to gum recession.
Hormones cause more blood flow to your gums, which leads the gums to overreact to different factors. High levels of estrogen and progesterone make women more sensitive to the presence of plaque.
Tobacco Products
Smokers and other tobacco users are more likely to develop sticky plaque, which can result in gum disease. Smoking causes a lack of oxygen in the bloodstream, and the infected gums do not heal well. This can eventually lead to receding gums.
Grinding and Clenching Your Teeth
Grinding or clenching your teeth puts excessive force on them, which can lead to gum recession.
Crooked Teeth or Misaligned Bite
When teeth don’t come together evenly, too much force can be exerted on the gums and surrounding bone, allowing damage to the gum tissue to occur.
Symptoms of Receding Gums
As receding gums progress over time, you may notice the following symptoms:
Long Teeth
One symptom is the visible lengthening of your teeth. When gums recede because of gum disease, teeth appear to be much longer than normal. Pockets can form due to gum recession, leaving you more susceptible to infections.
Exposed Roots
Exposed roots are another symptom of receding gums that can be extremely sensitive and uncomfortable. Root exposure usually happens because of gum disease or overbrushing, which is often attributed to incorrect brushing technique, hard bristles, or too much pressure.
Loose Teeth
If you have receding gums, you may notice loose teeth due to gum disease caused by bacteria accumulation under the gums around your teeth. As receding gums worsen, the gum pockets deepen.
Treatment for Receding Gums

Mild gum recession can be treated by professional deep cleaning in the affected area. During the deep cleaning, known as scaling and root planing, plaque and tartar are removed and the exposed root area is smoothed over, making it more difficult for bacteria to accumulate.
To treat advanced receding gums associated with periodontitis, a dental professional may recommend treatment with antibiotics in addition to scaling and root planing.
If deep cleaning is not sufficient to treat the condition because of excess bone loss and deep pockets, receding gums surgery may be required.
The surgery, known as a gum (or tissue) graft, may sound intimidating, but you don’t need to panic. During the procedure, root exposure is treated with graft tissue from your palate or your mouth.
However, gum surgery is not always necessary. Sometimes, tissue-simulating proteins are sufficient to encourage your body to grow bone and tissue, and in this case, you do not need a gum graft.
Preventing Receding Gums
To prevent receding gums, you should follow a good oral hygiene routine of brushing at least twice a day and flossing once a day.
Additional ways to prevent receding gums include:
- Quitting the use of tobacco products
- Eating a healthy, well-balanced diet
- Monitoring possible changes to your mouth
- Visiting your dental professional at least two times a year for professional cleanings and check-ups
Improve Dental Health with Oral-B

Most dental problems — including receding gums — can be prevented with a good oral hygiene routine that includes an electric toothbrush, like those in the Oral-B iO Electric Toothbrush Series.
A complete oral hygiene routine also includes daily flossing to clean the tight spaces between your teeth and below the gumline. Pairing your electric toothbrush with Oral-B Glide Floss can help you effectively remove stubborn plaque. The floss slides easily between teeth and is designed to be gentle on gums, which is important for preventing the plaque buildup that contributes to gum disease and recession.
The iO Series is the latest in oral care technology and is designed to remove 100% more plaque than a manual toothbrush.
Our electric toothbrushes give you the needed tools to get rid of bacterial plaque and food particles that contribute to cavities, gingivitis, and periodontitis. The tools include micro-vibrating bristles, a dentist-inspired round brush head, smart pressure sensors, and custom brushing modes.
With an effective oral hygiene routine and the Oral-B iO Electric Toothbrush Series, you can help stop receding gums before they start.
FAQs
-
Can gum recession be reversed?
-
What are the stages of gum recession?
-
How long does it take to heal from gum graft surgery?
Sources
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22753-gum-recession
- https://www.cdc.gov/oral-health/about/gum-periodontal-disease.html
- https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/gum-disease
- Grender, J., et al. (2020). An 8-week randomized controlled trial comparing the effect of a novel oscillating-rotating toothbrush versus a manual toothbrush on plaque and gingivitis. International Dental Journal, 70, S7–S15. https://doi.org/10.1111/idj.12571
- Li, Y., et al. (2024). Enhanced control of periodontitis by an artificial intelligence-enabled multimodal-sensing toothbrush and targeted mHealth micromessages: A randomized trial. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 51(12), 1632–1643. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13987
- Sutor, S., et al. (2025). Effect of a powered and a manual toothbrush in subjects susceptible to gingival recession: A 36-month randomized controlled clinical study. International Journal of Dental Hygiene, 23(1), 26–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/idh.12834
- Zou, Y., et al. (2024). A meta-analysis comparing toothbrush technologies on gingivitis and plaque. International Dental Journal, 74(1), 146-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.identj.2023.06.009
Table of Contents
- What are Receding Gums?
- Causes of Receding Gums
- Symptoms of Receding Gums
- Treatment for Receding Gums
- Preventing Receding Gums
- Improve Dental Health with Oral-B
-
- FAQs
- Sources

Sign Up
for gum care tips, expert advice, and exclusive offers.

Sign Up
for gum care tips, expert advice, and exclusive offers.