Scaling and Root Planing: Procedure, Benefits, and Aftercare Tips
Summary
Key Takeaways
- Scaling and Root Planing is a deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline. It smooths the tooth roots to promote healing.
- The procedure is an effective treatment for gum disease, which helps prevent tooth loss and maintain good oral health.
- Proper aftercare is crucial for healing and includes gentle brushing and using a recommended mouthwash.
- Recovery can also be helped by eating soft foods and staying hydrated.
- Make sure you attend all follow-up appointments.
Table of Contents

This blog has been reviewed and approved by Dr Robert Lee, a dental professional of 35 years
LEARN MORE >Key Takeaways
What Is Scaling and Root Planing?
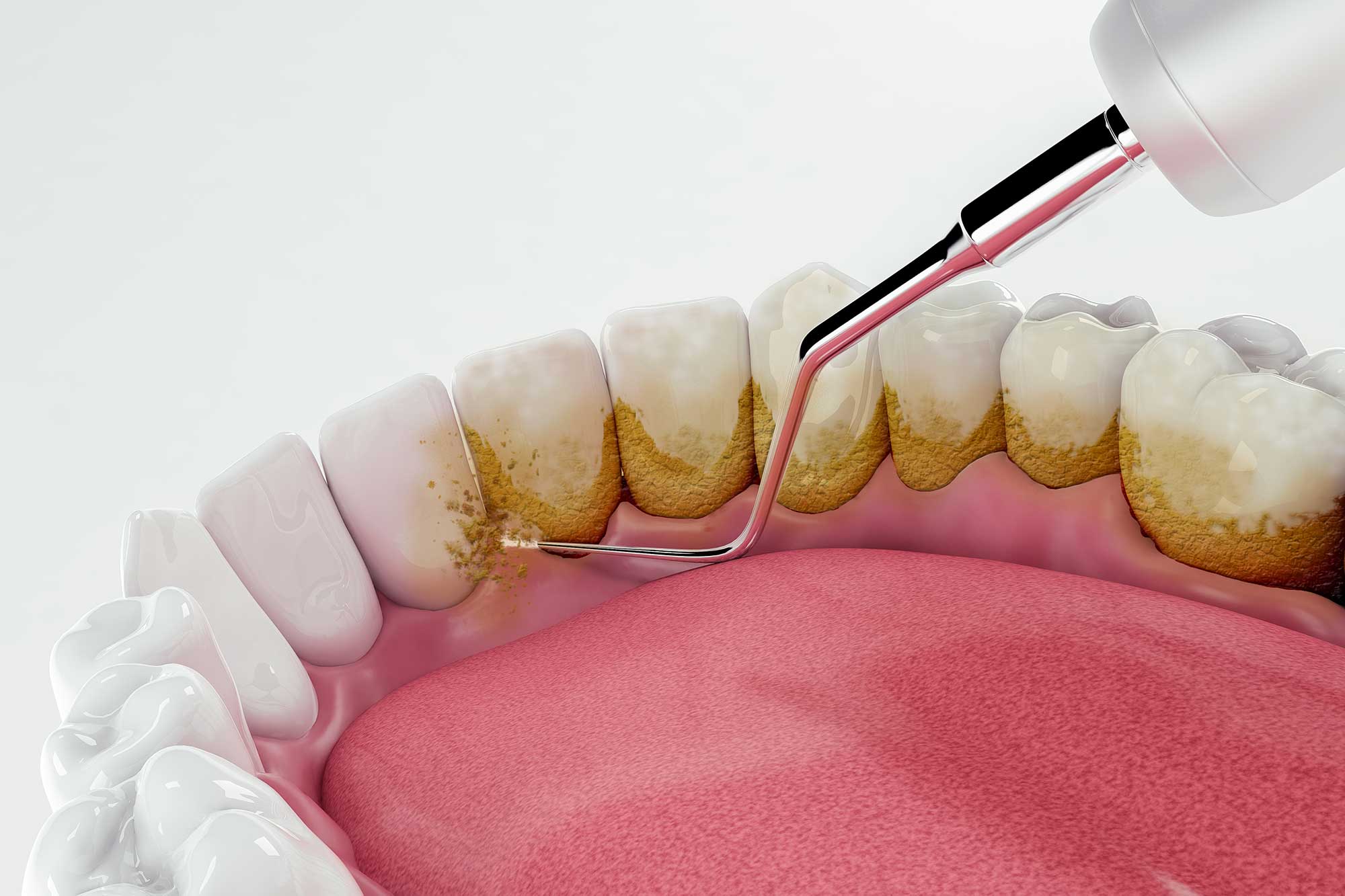
Scaling and root planing is a two-step dental procedure aimed at treating periodontitis (gum disease), particularly after it has progressed beyond the initial stage of gingivitis.
It's essentially a deep cleaning that reaches deeper beneath your gums.
Scaling
- Involves the removal of plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline
- Crucial because plaque and tartar harbor bacteria that can led to gum inflammation and infection
- Helps reduce the bacterial load in the mouth
Root Planing
- Follows scaling, focuses on the tooth roots
- The dentist or dental hygienist smooths the roots to remove any remaining tartar and eliminate rough spots where bacteria can accumulate
- Helps the gums reattach more firmly to the teeth and promotes better stability
Why Is Scaling and Root Planing Important?
Gum disease is a leading cause of tooth loss in adults. It begins with gingivitis and causes swollen, bleeding gums. It can progress to periodontitis where gums pull away from the teeth and pockets form that become infected. Left untreated, can lead to bone loss and tooth mobility. Scaling and root planing are effective treatments for gum disease. Thoroughly cleaning the roots helps:
- Eliminate infection
- Reduce gum inflammation
- Promote the healing of gum tissues
- Improve oral health
- Prevent the progression to more severe forms of gum disease
Scaling and Root Planing Procedure
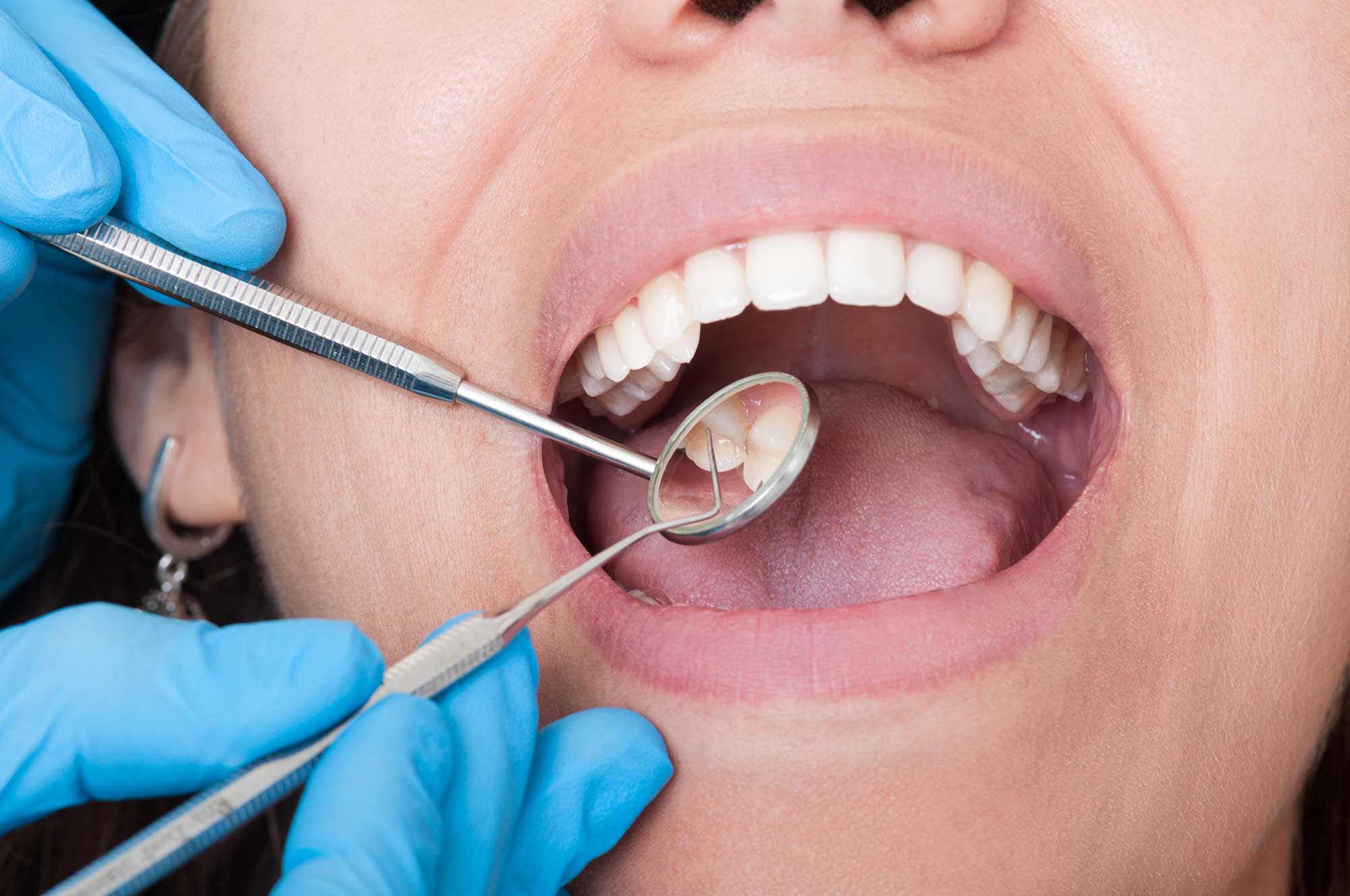
- A topical or local anesthetic is given to numb the area
- Plaque and tartar (scale) is scraped from your teeth, both above and below the gumline down to the periodontal pocket
- The rough surfaces on the roots of the teeth are smoothed (planing) which helps the gums reattach to the teeth
- Antibiotics might be placed directly into the periodontal pockets, and oral antibiotics might be prescribed to take after the procedure.
Aftercare Tips for a Smooth Recovery
Proper aftercare is crucial for effective healing and to maintain the benefits of the procedure.
Follow Proper Oral Hygiene Practices
- Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Be gentle around the treated areas to avoid causing further irritation or damage to the gums
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline
Use a Gentle Mouthwash
- Use a mild, alcohol-free mouthwash. Gentle, antimicrobial mouthwashes can help reduce bacteria and promote healing
- Mouthwashes that contain alcohol can cause dryness and irritation to sensitive gum tissue
Eat Soft Foods
- For the first few days following scaling and root planing eat foods that are gentle on the gums
- Food like yogurt, mashed potatoes, scrambled eggs and soups will help to avoid putting pressure on your gums
- Avoid hard, crunchy, and spicy foods that can cause discomfort and delay healing
Stay Hydrated
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day, which keeps your mouth hydrated and washes away food particles and bacteria
Avoid Irritants
- Avoid smoking and alcohol which can irritate the gums and delay healing
- Avoid acidic beverages like citrus juices and sodas that can cause discomfort
Manage Sensitivity and Discomfort
- To manage sensitivity to hot and cold foods and drinks, use a desensitizing toothpaste
- Avoid consuming extremely hot or cold foods and drinks
- Take any medications recommended by your dentist regularly
Avoid Intense Physical Activity
- Avoid strenuous physical activity for at least 24 hours after the procedure
- Allow your body to focus on healing and prevents any bleeding or discomfort caused by increased blood flow
Attend Follow-Up Appointments and Routine Checkups
- Ensures the scaling and root planing treatment was effective
- Allows any complications to be detected and addressed before they become serious
- Is a good way to monitor your overall oral health
Risks and Benefits
Like so many things when it comes to oral health, there are both risks and benefits to scaling and root planing. The benefits tend to outweigh any risks.
Benefits
- Prevent tooth loss and gum recession
- Reduce your risk for advanced gum disease
- Gets rid of the oral bacteria that causes halitosis (bad breath)
- Improve overall health by reducing harmful bacteria in your mouth that can travel through your bloodstream to other parts of your body
Risks
- Bleeding: Some bleeding is normal after the procedure. Let your dentist or dental hygienist know if you have excessive bleeding that doesn’t stop.
- Gum Recession: If your gums were swollen before your scaling and root planing, they will shrink back once the infection is gone. Because of this, you might see a little more of your teeth roots.
- Infection: Scaling and root planing can introduce harmful bacteria into your bloodstream, which could lead to bacteremia or blood infection. Prescribed antibiotics or mouth rinse can reduce this risk.
- Loose Teeth: Your teeth might feel a little loose immediately after the procedure. This should go away once your gums heal and tighten back up.
- Teeth Sensitivity: Removing plaque and tartar can make your teeth more sensitive to heat and cold. This sensitivity should go away in a month or two.
- Tenderness: Your gums might feel a little sore for a couple of days. Taking over-the-counter pain relievers can manage discomfort.
Summary
Scaling and root planing are a crucial procedure for treating gum disease and preventing more serious dental and health issues. By removing plaque and tartar from under the gums and smoothing tooth roots, this deep cleaning helps gums heal and reattach to teeth.
Starting with a local anesthetic, the procedure involves scraping plaque and tartar from your teeth both above and below your gums. Rough tooth roots are then smoothed out. The process takes one to two hours to complete and may be done in one appointment, or split into two, with few risks or complications.
Afterwards, the patient may be given prescribed antibiotics to help prevent infection and can use over-the-counter pain medications to help with discomfort. Apart from avoiding strenuous activities for 24 hours and eating soft foods for the first few days, you can return to your daily routine. With proper aftercare, including maintaining routine dental checkups, most patients experience a smooth recovery and improved oral health.
Oral-B Knows That Healthy Gums Are the Foundation of a Healthy Mouth
Healthy gums are crucial to tooth and mouth health. In the event of gum disease (also known as gingivitis), the first line of defense is to see a dental professional. They can do a proper examination, determine the level of periodontal disease, and recommend treatments. But there are things you can do to help.
- Oral-B iO electric toothbrushes help protect against tooth and gum issues. For existing gum problems, they have been shown to be more effective than a manual toothbrush and certain sonic toothbrushes. Additionally, when used with its brush tracking app, the Oral-B iO can help users manage even advanced gum issues more effectively.
- Crest Gum Detoxify is an advanced stannous fluoride toothpaste. When used as part of your daily routine, its activated foam helps neutralize harmful plaque bacteria even in hard-to-reach areas. It is clinically proven to lead to healthier gums.
- The Oral-B iO Gentle Care replacement brush head features over 4,000 thin, high-density bristles that adapt to the curve of the tooth for a gentle, effective clean. When paired with the iO toothbrush, it provides a superior clean along the gumline compared to a regular manual toothbrush.
- Crest Pro-Health Multi-Protection Mouthwash is clinically proven to provide 24-hour protection against plaque and gingivitis when used twice daily.
- Oral-B Glide Pro-Health Deep Clean Floss’s microtextured fiber removes plaque and helps prevent gingivitis as part of a complete dental plan.
FAQs
-
Does scaling and root planing hurt?
-
How long does scaling and root planing take?
-
How much does scaling and root planing cost?
-
How long after scaling and root planing can I eat?
-
Do I need to have scaling and root planing done regularly?
-
Should everyone get scaling and root planing?
Sources
- https://www.ada.org/sitecore/content/ADA-Organization/ADA/MouthHealthy/home/all-topics-a-z/scaling-and-root-planing
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/23983-tooth-scaling-and-root-planing
- https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/what-to-know-about-periodontal-scaling-and-root-planing
Biesbrock, A., et al. (2019). The effects of bioavailable gluconate chelated stannous fluoride dentifrice on gingival bleeding: Meta-analysis of eighteen randomized controlled trials. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 46(12), 1205–1216. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13203
Thurnay, S., et al. (2022). A Global, In-Market Evaluation of Toothbrushing Behaviour and Self-assessed Gingival Bleeding with Use of App Data from an Interactive Electric Toothbrush. Oral Health & Preventive Dentistry, 20, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3290/j.ohpd.b2572911
Zou, Y., et al. (2024). A meta-analysis comparing toothbrush technologies on gingivitis and plaque. International Dental Journal, 74(1), 146-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.identj.2023.06.009
Table of Contents
- What Is Scaling and Root Planing?
- Why Is Scaling and Root Planing Important?
- Scaling and Root Planing Procedure
- Aftercare Tips for a Smooth Recovery
- Risks and Benefits
- Summary
- Oral-B Knows That Healthy Gums Are the Foundation of a Healthy Mouth
-
- FAQs
- Sources

This blog has been reviewed and approved by Dr Robert Lee, a dental professional of 35 years
LEARN MORE >
Sign Up
for oral care tips, expert advice, and exclusive offers.

Sign Up
for oral care tips, expert advice, and exclusive offers.



