What Are Dental Caries? Treatments, Signs, and Symptoms
Summary
Key Takeaways
- Early detection through regular dental check-ups help identify and address dental caries before they progress
- Prevention is key. Effective preventive measures include regular brushing and flossing. limiting sugary foods, and using fluoride products
- Timely treatment can address cavities promptly, prevent more serious dental issues, and preserve tooth form and function
- Healthy lifestyle choices and good habits play a crucial role in preventing dental caries. These include eating a balanced diet and good oral hygiene practices
Table of Contents

This blog has been reviewed and approved by Dr Robert Lee, a dental professional of 35 years
LEARN MORE >Key Takeaways
What Are Dental Caries?
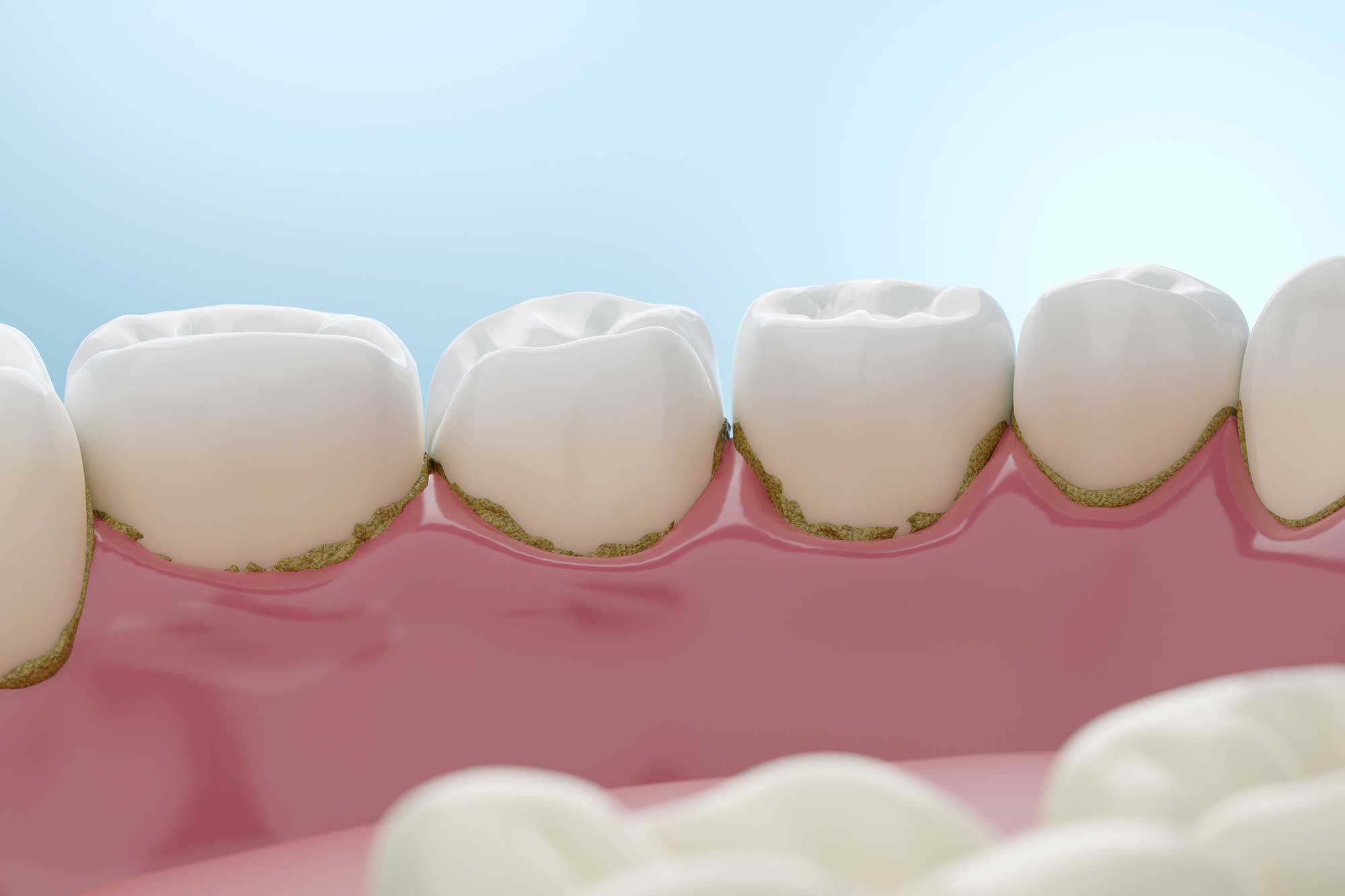
“Dental Caries” is the medical term for tooth decay or cavities. Caries occur when harmful bacteria in your mouth feed on sugars and starches from the foods and drinks you consume. Those bacteria produce acids that gradually weaken (or demineralize) tooth enamel. Over time, this process can lead to holes or cavities in your teeth.
Dental Caries Signs and Symptoms
Early-stage tooth decay doesn’t usually cause noticeable symptoms. However, as decay progresses, symptoms include:
- Tooth Sensitivity: Discomfort or pain when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods and beverages
- Early Sign - White Spots: The first sign of caries can be a chalky white spot on the tooth where minerals have been lost.
- Progression to Cavities: As decay progresses, these spots may become light brown and eventually develop into visible dark spots, pits, or holes on the surface of your teeth.
- Toothache: Persistent pain in a tooth that worsens when chewing or touching the tooth
- Swelling or Abscess: In advanced cases, an infection can cause swelling in the face or jaw. A pocket of pus and abscess may form.
If you notice any of these symptoms, promptly consult a dentist or dental hygienist to prevent further damage.
Treatment Options
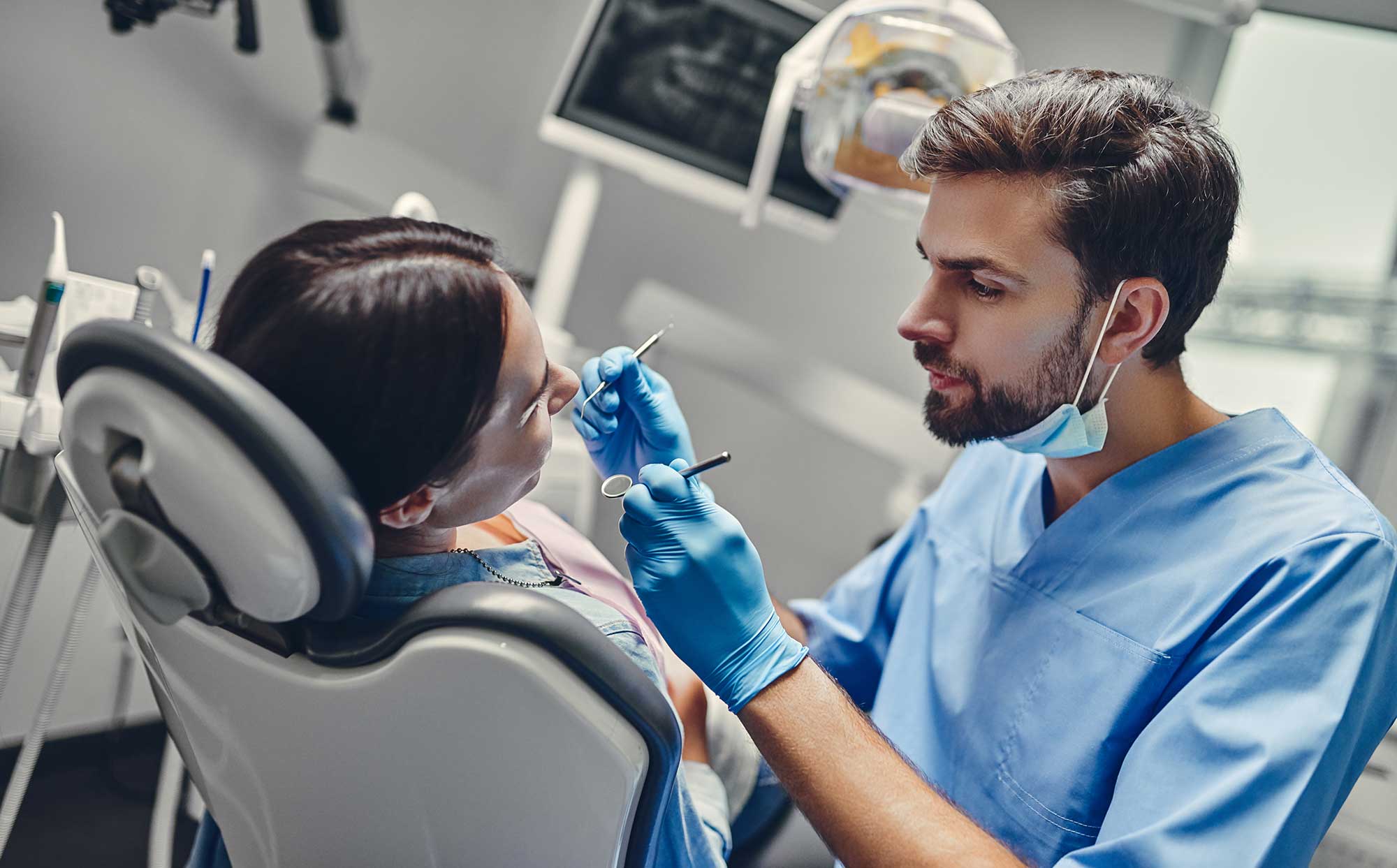

Regular dental visits are crucial for the early detection and treatment of dental caries. Treatment for dental caries depends on the severity of the tooth decay.
- Fluoride Treatments: Fluoride can help remineralize tooth enamel and help reverse minor decay
- Fillings: A dentist removes the decayed portion of the tooth and fills it with composite resin, amalgam, or porcelain restoration
- Crowns: If a large portion of the tooth is decayed, a crown may be placed over the tooth to restore its shape and function
- Root Canals: When decay reaches the soft tissue inside the tooth, called the pulp, a root canal may be necessary to remove the infected tissue, seal and save the tooth
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases where the tooth cannot be saved, extracting the tooth may be the last resort
Preventing Dental Caries
- Brush Regularly: Brushing with fluoride toothpaste at least twice a day strengthens tooth enamel and helps prevent cavities
- Floss Daily: Helps remove food particles and plaque between your teeth that your toothbrush can’t reach
- Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks: Reduce the amount of sugary snacks and beverages you consume because they contribute to acid production by bacteria
- Use Fluoride Products: Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel and prevents tooth decay
- Regular Check-ups: See your dentist and dental hygienist regularly for professional cleanings and exams. This helps issues to be diagnosed and addressed early, helping to prevent serious problems down the road
- Consider Sealants: Protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth, they help prevent cavities on teeth that are harder to brush effectively
Summary
Dental caries, commonly known as cavities, are a common yet preventable dental issue caused by the interaction of bacteria and sugars in the mouth. Dental caries is the disease process caused by the interaction of bacteria and sugars that results in tooth decay. Recognizing early signs, such as tooth sensitivity or pain and noticing holes or pits in a tooth, is an important step in stopping damage. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the tooth decay. These range from fluoride treatments to remineralize the tooth’s enamel to fillings and root canals for advanced decay. Tooth extraction may be warranted for the most severe cases. Practicing good oral hygiene through regular brushing and flossing as well as limiting sugary substances are the best ways to significantly reduce dental caries.
Avoid Cavities, Tooth Decay and Tartar with Oral-B
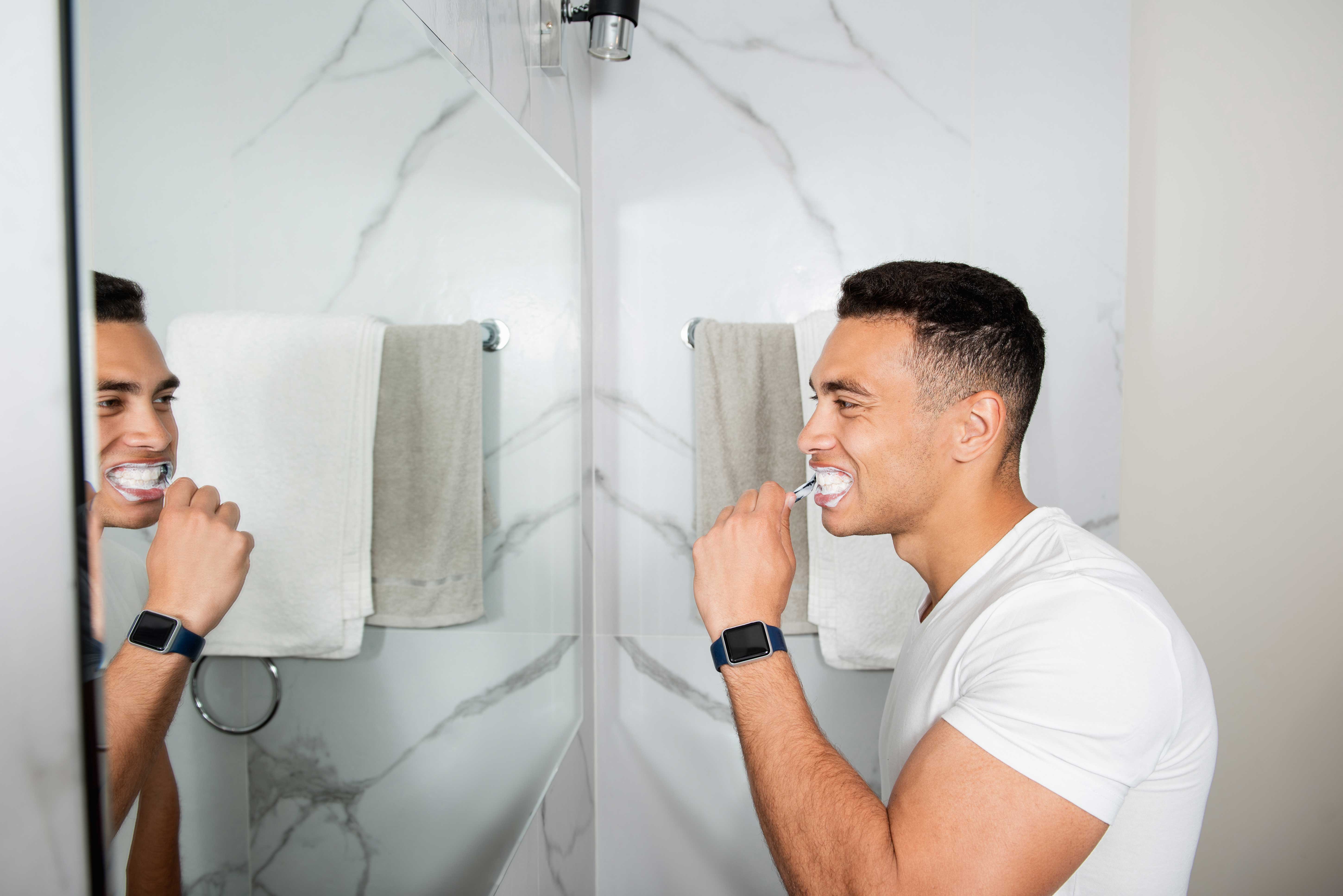

Keep your teeth clean and cavity-free. Things like tooth decay and tartar happen when plaque forms on teeth as a sticky film. Plaque contains bacteria that feed on sugar from food and drinks. As these bacteria metabolize sugar, they release acids that can erode tooth enamel. This can lead to cavities and other problems. But help is just a toothbrush away. Here are a few suggestions to help establish a regular, effective routine.
- Try switching to an electric toothbrush, such as the Oral-B iO electric toothbrush, which is scientifically proven to protect teeth and gums from the leading causes of tooth decay, gum disease, and tooth loss.
- The right toothbrush head, such as the Oral-B iO Ultimate Clean brush head, removes plaque and has different bristle lengths that reach deep into the spaces between your teeth, where plaque bacteria love to hide.
- Combine with a Crest toothpaste containing fluoride. For powerful protection against plaque, gingivitis, and cavities, Crest Pro-Health Toothpaste is formulated with stannous fluoride. For a classic option focused on cavity prevention, Crest Cavity Protection Toothpaste uses sodium fluoride.
- To further protect your teeth, swish with a therapeutic mouthwash like Crest Pro-Health Gum Care Mouthwash, which helps neutralize plaque germs that can lead to cavities.
- To help prevent tooth decay and reduce your risk of developing gum disease by removing plaque, floss your teeth at least once daily with Oral-B floss, and make sure you get around every tooth. Another easy add-on to help your oral care and prevent cavities from forming is to use an Oral-B water flosser.
There is a connection between oral health and systemic health. That’s why Oral-B, in partnership with Crest, is committed to championing oral health for all, conducting research and creating products to help with a wide range of oral health conditions. Oral-B products are scientifically proven to protect teeth and gums from the leading causes of tooth decay, gum disease, and tooth loss.
FAQs
-
Can dental caries be reversed?
-
What do dental caries look like?
-
What is the difference between caries and cavities?
-
Is there a way to assess my risk of getting dental caries?
-
Can I get a vaccine for dental caries?
Sources
- https://www.ada.org/resources/ada-library/oral-health-topics/caries-risk-assessment-and-management
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10946-cavities
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/tooth-decay-caries-or-cavities
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cavities/symptoms-causes/syc-20352892
- https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/tooth-decay/more-info/tooth-decay-process
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8757708/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31518435/
- https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/dental-health-cavities
- Grender J, Goyal CR, Qaqish J, Adam R. An 8-week randomized controlled trial comparing the effect of a novel oscillating-rotating toothbrush versus a manual toothbrush on plaque and gingivitis. International Dental Journal 2020; 70: S7–S15
- Chen CK et al. Association between chronic periodontitis and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease: A retrospective, population-based, matched-cohort study. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy 2017; 9:56.
- Grossi SG et al. Periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus: A two-way relationship. Ann Periodontol 1998;3:51-61.
- Janket SJ et al. Meta- analysis of periodontal disease and risk for coronary heart disease and stroke. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2003; 95:559-569.
- Ganss, Carolina, et al. "Tooth brushing motion patterns with manual and powered toothbrushes—a randomised video observation study." Clinical oral investigations 22 (2018): 715-720
Y Zou, J Grender, R Adam, L Levin, A meta-analysis comparing toothbrush technologies on gingivitis and plaque, International Dental Journal, 2024, 74(1), 146–156. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.identj.2023.06.009
Table of Contents
- What Are Dental Caries?
- Dental Caries Signs and Symptoms
- Treatment Options
- Preventing Dental Caries
- Summary
- Avoid Cavities, Tooth Decay and Tartar with Oral-B
-
- FAQs
- Sources

This blog has been reviewed and approved by Dr Robert Lee, a dental professional of 35 years
LEARN MORE >
Sign Up
for oral care tips, expert advise, and exclusive offers.

Sign Up
for oral care tips, expert advise, and exclusive offers.


