Gingivitis Vs Periodontitis: What's The Difference

SUMMARY
Key Takeaways
- Gingivitis and periodontitis are conditions of gum disease.
- Gingivitis is the first stage of gum disease that can be reversed, and periodontitis is a more severe stage of gum disease that can’t be fully reversed.
- Symptoms of gum disease include redness and bleeding gums.
- Your dentist or dental hygienist may recommend a deep dental teeth cleaning to help gum health.
- Taking care of your oral hygiene and brushing and flossing daily and using a water flosser can help your overall gum health!
Table of Contents

This blog has been reviewed and approved by Dr Robert Lee, a dental professional of 35 years
LEARN MORE >Key Takeaways
- Gingivitis and periodontitis are conditions of gum disease.
- Gingivitis is the first stage of gum disease that can be reversed, and periodontitis is a more severe stage of gum disease that can’t be fully reversed.
- Symptoms of gum disease include redness and bleeding gums.
- Your dentist or dental hygienist may recommend a deep dental teeth cleaning to help gum health.
- Taking care of your oral hygiene and brushing and flossing daily and using a water flosser can help your overall gum health!
Your gums are just as important to take care of compared to your teeth! Gum disease can come in different forms and your dentist and dental hygienist may refer to it as different conditions, such as gingivitis and periodontitis. Both relate to gum disease, however gingivitis usually happens first as an initial stage and then progresses into a more advanced gum disease known as periodontitis. Read on to learn more about the difference and view tips from Oral-B to maintain your oral hygiene.
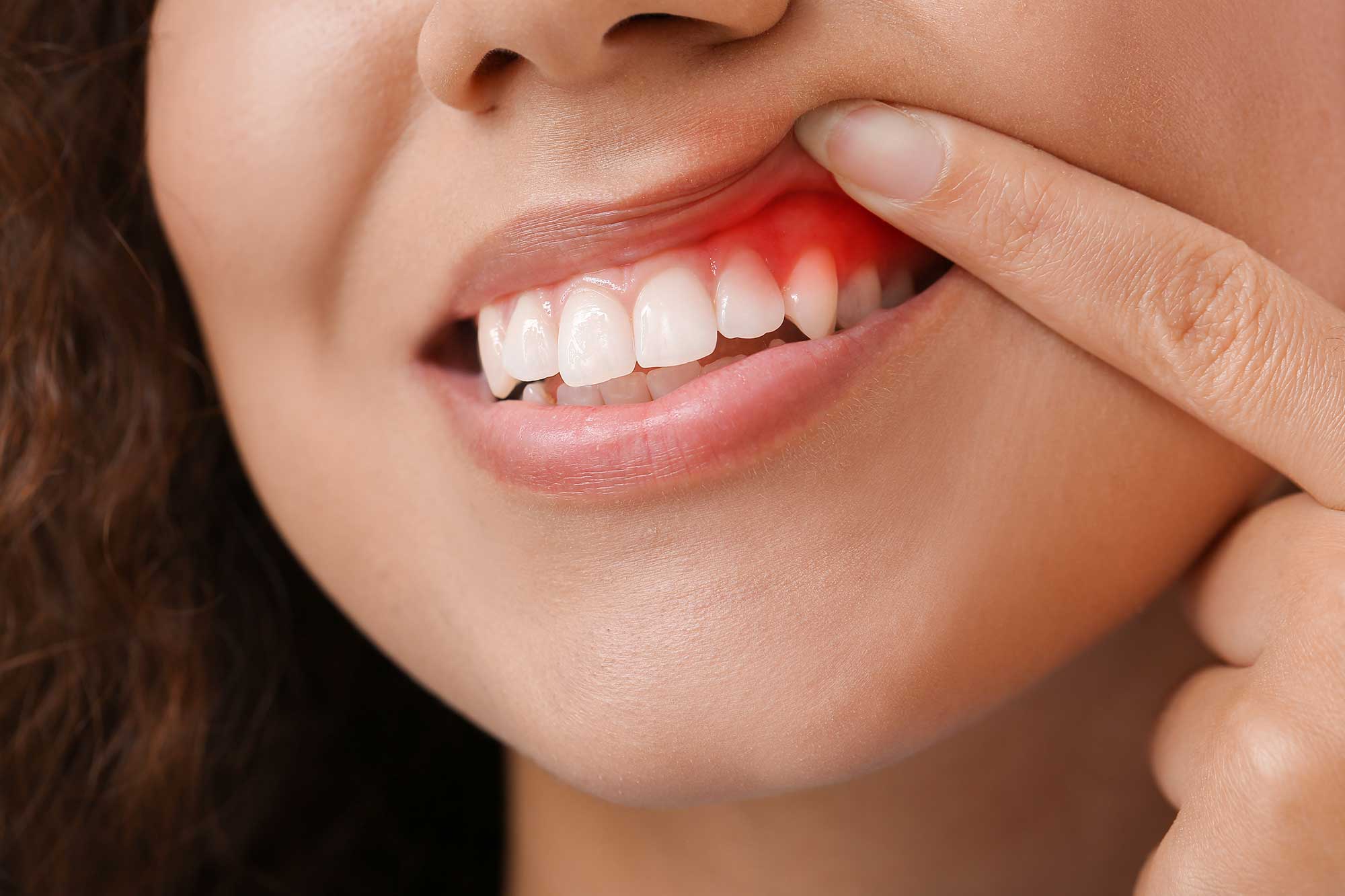
Gingivitis vs Periodontitis
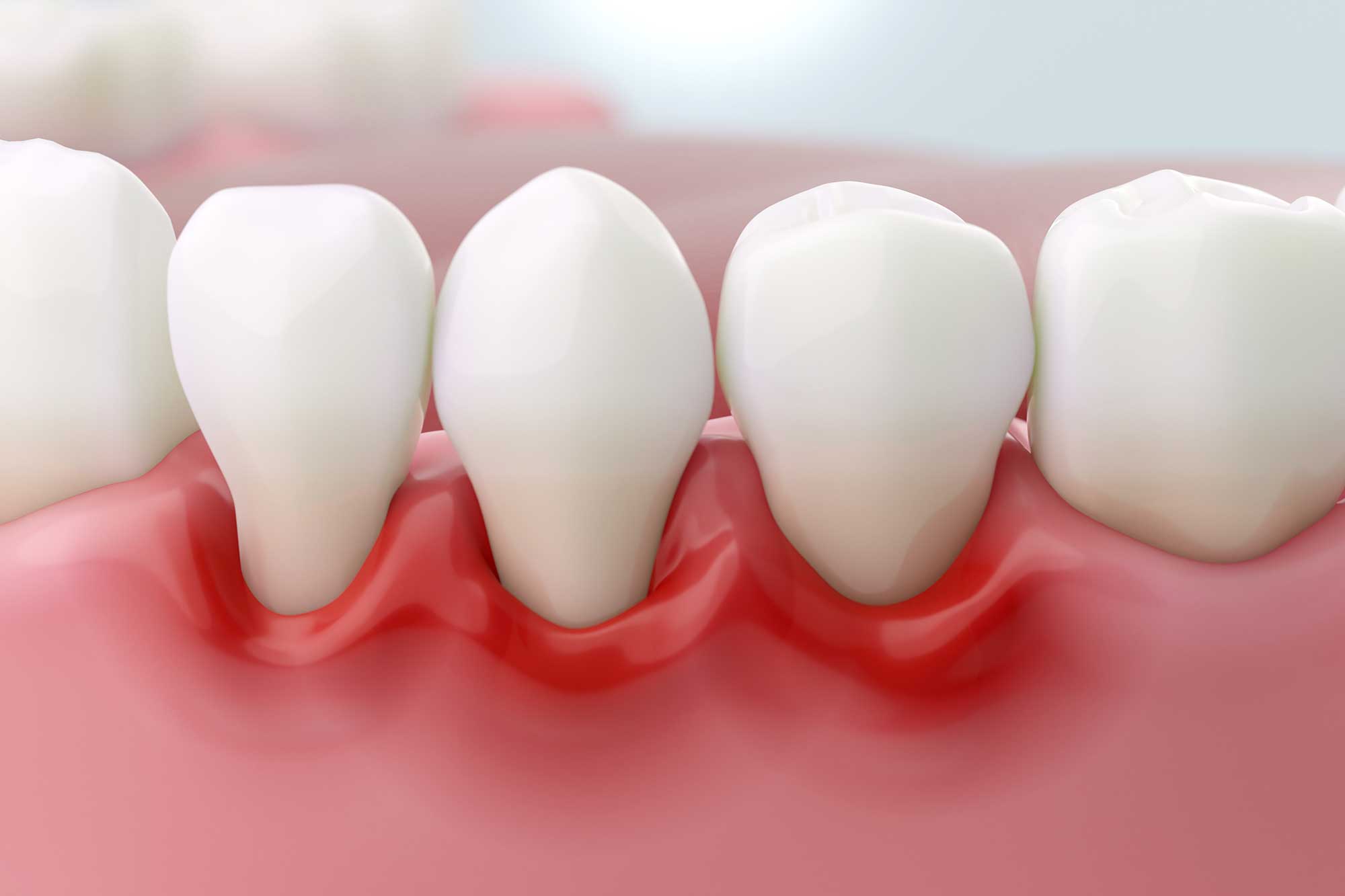
Gingivitis is a form of gum inflammation and gum disease and can be treated. However, gingivitis can become more severe and progress into periodontitis. Both gingivitis and periodontitis can be treated with good oral care and regular visits to your dental professionals for dental cleanings. However, unlike gingivitis, periodontitis can only be managed, not reversed.
- Gingivitis: can come and go and shows up as gum inflammation or gum bleeding.
- Periodontitis: more advanced gum disease and inflammation, that can lead to losing teeth overtime and can only be managed, but not reversed.
Periodontitis is when the periodontium, the structure of hard and soft tissues that surround teeth, gets inflamed. The tissues that help protect the root of a tooth may begin to recede and this can lead to tooth loosening. If gums recede too much it can cause more inflammation in the gums and create space for infections to form. Periodontitis is more severe, and a more concerning condition compared to gingivitis and should be treated by a dentist or dental hygienist immediately.
A dentist or dental hygienist will typically need x-rays and photos of your teeth and gum lines to determine periodontitis and how severe it is and to know how to treat it. Your dental professional will give you advice on how to take care of your oral hygiene and how to brush properly to prevent gingivitis and periodontitis.
Gingivitis vs Periodontitis Symptoms
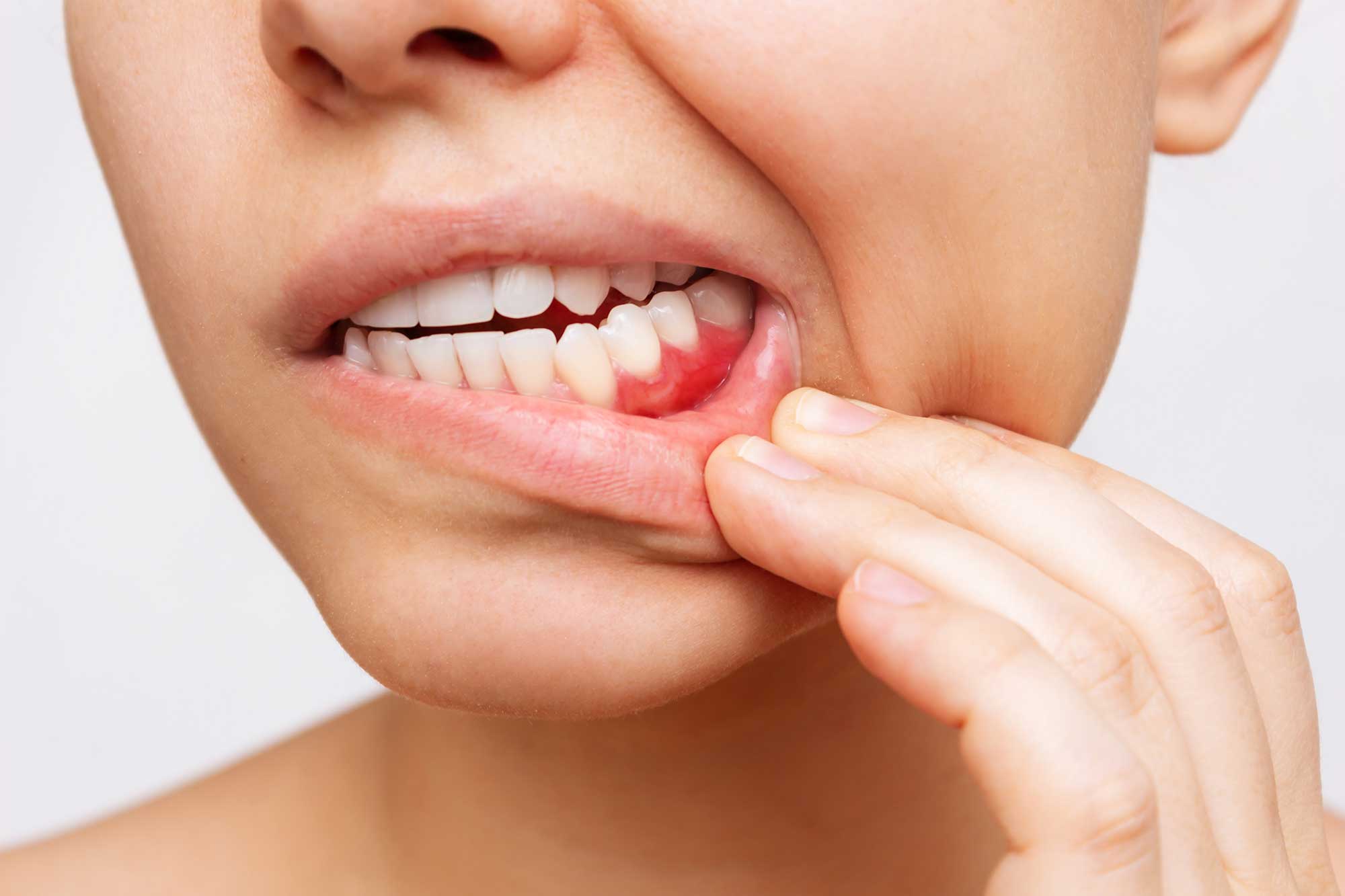
At first gingivitis and periodontitis may go unrecognized and the symptoms may vary depending on how severe the condition becomes. If you notice inflamed, reddish gums or have tooth sensitivity be sure to get to your dental professional.
Here are some signs and symptoms of gingivitis and periodontitis:
Gingivitis Symptoms
- Swollen, inflamed gums
- Reddish gums (vs pinkish)
- Gum bleeding
- Sensitive teeth
- Bad breath
Periodontitis Symptoms
- Gum bleeding
- Sensitive teeth
- Receding gums
- Loose teeth
- Pain with chewing
- Bad breath
Gingivitis and Periodontitis Treatment
A dentist or dental hygienist can diagnose gingivitis and periodontitis and advise you on the best treatment. However, when treating both, there is a focus on reducing gum inflammation and having proper oral care. Treatment tips to help manage your gums’ signs and symptoms of gingivitis and periodontitis:
- Routine professional dental cleanings will keep plague off your teeth and gums and allow your dentist and dental hygienist to monitor your gum health.
- Deep teeth cleaning is often recommended if you have signs and symptoms of gingivitis or periodontitis, to reduce swollen gums and clean below the gumline.
- Certain antibacterial mouthwashes may be recommended depending on your condition.
- Use an electric toothbrush and brush and floss daily.
- Your dental professional will share other recommendations to remove plaque and tartar and keep your gums healthy.
Periodontitis is a more severe condition, and your dental professional may recommend surgery, antibiotics and other treatments to help your condition.
Oral Care to Help Gum Health
Healthy gums are crucial to tooth and mouth health. In the event of gum disease (also known as gingivitis), the first line of defense is to see a dental professional. They can do a proper examination, determine the level of periodontal disease, and recommend treatments. But there are things you can do to help.
- When you brush with Oral-B iO electric toothbrushes, you can protect your gums and help prevent further gum recession. Oral-B iO helps you avoid new tooth and gum issues—and if you have existing gingivitis, it can resolve it quicker than a manual toothbrush.
- The right toothbrush head, such as the Oral-B iO Gentle Care brush head, contain dentist-inspired soft bristles and optimized bristle patterns that adapt to the curves of the teeth and gums and provide a gentle clean with maximum comfort.
- Crest Toothpaste contains stannous fluoride which fights the plaque bacteria that cause gum disease. Pair that with an Oral-B iO electric toothbrush to help stop gum bleeding and other signs of early gum disease.
- Mouthwash can be an important part of your daily oral health routine. The best mouth rinses, like Crest Mouthwash, are clinically proven to provide 24-hour protection against plaque and gingivitis with 2x daily use.
- Dental floss, used daily, helps prevent gingivitis as part of a complete dental plan. Look for a floss that can fit more easily into tight spaces, such as Glide Floss.
There is a connection between oral health and systemic health. That’s why, beyond helping with issues such as tooth decay, gum disease and tooth loss, our products can help prevent and reduce plaque bacteria before they spread to other parts of the body.
FAQs
-
How long until gingivitis turns into periodontitis?
-
Can gingivitis heal on its own?
-
How do you tell if you have periodontitis or gingivitis?
-
Can you reverse periodontitis?
-
Does salt water help gingivitis?
-
What does stage 1 gingivitis look like?
Sources
- https://www.healthline.com/health/dental-and-oral-health/gingivitis-vs-periodontitis#what-is-periodontitis
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279593/
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/gingivitis-vs-periodontitis#causes-and-risk-factors
- McCains, V. (2024) Healthy Mouth, Healthy Body. National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research News.
Adam, R., et al. (2025). A 4-week randomized clinical trial evaluating plaque and gingivitis effects of a new oscillating-rotating electric toothbrush. Journal of the American Dental Association (1939), 156(8), 611–619.e2.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adaj.2025.04.015.
Chen, C. K., et al. (2017). Association between chronic periodontitis and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease: A retrospective, population-based, matched-cohort study. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, 9, 56.https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-017-0282-6.
Grossi, S. G., et al. (1998). Periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus: A two-way relationship. Annals of Periodontology, 3, 51-61.https://doi.org/10.1902/annals.1998.3.1.51.
He, T., et al. (2024). Relationship between 1-, 3-, and 6-Month Gingival Bleeding Outcomes. JDR Clinical and Translational Research, 9(3), 286–293.https://doi.org/10.1177/23800844231206387.
Janket, S. J., et al. (2003). Meta-analysis of periodontal disease and risk for coronary heart disease and stroke. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology, 95, 559-569.https://doi.org/10.1067/moe.2003.107.
Pitchika, V., et al. (2021). Impact of Powered Toothbrush Use and Interdental Cleaning on Oral Health. Journal of Dental Research, 100(5), 487–495.https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034520973952.
Sutor, S., et al. (2025). Effect of a powered and a manual toothbrush in subjects susceptible to gingival recession: A 36-month randomized controlled clinical study. International Journal of Dental Hygiene, 23(1), 26–36.https://doi.org/10.1111/idh.12834.
Table of Contents
- Gingivitis vs Periodontitis
- Gingivitis vs Periodontitis Symptoms
- Gingivitis and Periodontitis Treatment
- Oral Care to Help Gum Health
-
- FAQs
- Sources

This blog has been reviewed and approved by Dr Robert Lee, a dental professional of 35 years
LEARN MORE >
Sign Up
for gum care tips, expert advice, and exclusive offers.

Sign Up
for gum care tips, expert advice, and exclusive offers.



