When Do Babies Start Teething: Symptoms and Remedies

Summary
Table of Contents

This blog has been reviewed and approved by Dr Robert Lee, a dental professional of 35 years LEARN MORE >
Baby teething can be uncomfortable, leaving gums sore and causing increased fussiness. Understanding when teething typically begins and implementing appropriate soothing techniques can help alleviate discomfort and support your baby during this phase.
When do Babies Start Teething
Every baby is unique, but babies typically begin teething between 4 months and 7 months. However, sometimes your baby’s first teeth appear around 3 months, other babies it’s after their first birthday. It’s alright if your baby is “behind” or “ahead” because babies develop at their own pace. Once that first tooth comes in, it’s time to start brushing! Gently brush with a soft-bristled toothbrush that’s designed specifically for kids’ small mouths and a fluoride-free training toothpaste. We recommend the Oral-B and Crest Baby Training Toothpaste and Toothbrush Kit.
Which Baby Teeth Come In First?
Most babies first get their bottom two front teeth. These are soon followed by the top front teeth. Read more about baby teeth eruption here: ‘Teeth Eruption Chart’.
Did you know? The rate of teething is typically about four teeth every six months. Also, teeth emerge somewhat symmetrically – a tooth on the right and its corresponding left tooth will appear around the same time.
Baby Teeth Eruption Chart
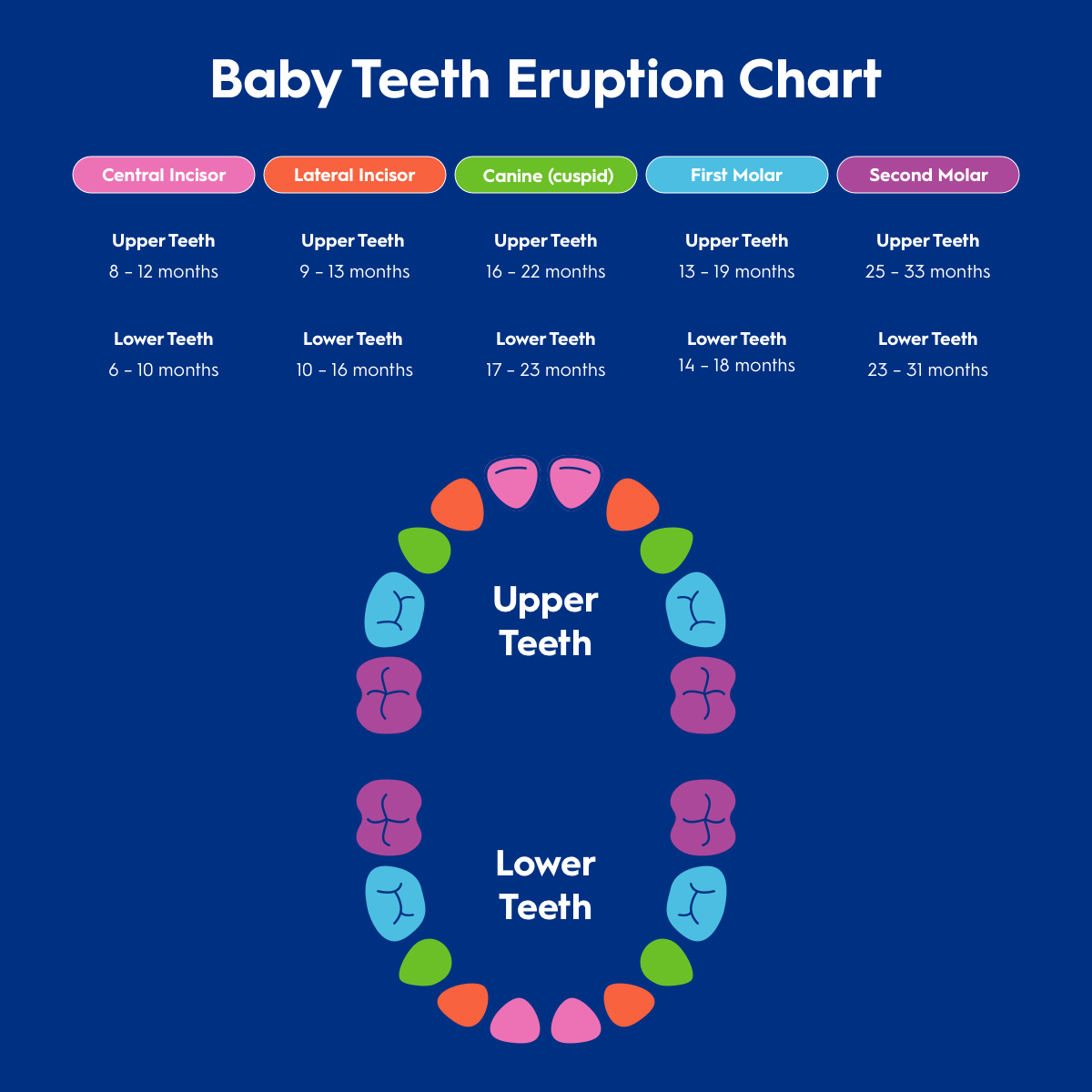
How many Teeth do Babies have?
Babies have 20 primary teeth. Adults, meanwhile, have 32.
How long does Teething last?
After first emerging between 4 and 7 months, your baby’s primary teeth will continue “erupting” until they’re two-and-a-half or 3. Adult teeth will start replacing the primary or baby teeth around age 5 or 6.
Most of your child’s adult teeth should be fully erupted by the age of 13, except the third molars, also known as wisdom teeth which come in around the late teens or early twenties.
Signs of Teething In Babies
Wouldn’t it be wonderful if your baby could tell you they’re teething? But of course, talking is still a long way off. For that reason, you’ll have to look for signs your baby is teething. These signs include:
- Unexplained Crying: If your baby is crying and they’re not hungry, tired, or in need of a diaper, and they’re in the age range, they may be teething.
- Drooling More Than Usual: Excessive drooling is another common sign that your baby is teething, and much more precise than crying, which can mean many different things.
- Low Fever: Teething can sometimes result in a low-grade fever of less than 101°F.
- Face Redness or Face Rash: It’s common for teething babies to develop redness or a more pronounced rash on the side of the face due to the excessive amount of drool.
- Biting Hard Items: Often babies will try to sooth teething by chewing on hard items, such as a building block. If your baby is suddenly very interested in chewing on things, they may be teething.
- Tender Gums: If you think your baby is teething, look inside their mouth. Do their gums look red, swollen, or tender? If so, expect some teeth to start peeking through soon.
- Disturbed Sleep: Teething soreness can also make it difficult for your baby to fall asleep or stay asleep. If your baby has been sleeping soundly and suddenly wakes up, or if their sleeping patterns are particularly disjointed, teething may be a cause.
Remedies for Soothing Teething Baby
As baby teeth come in, your baby’s tender gums become quite sore. This can lead to crying, crankiness, and significantly less sleep for everyone involved! If your teething baby needs additional soothing, here’s a few things to try:
- Rub Baby’s Gums: Gently massage baby’s gums with a clean finger or wet gauze.
- Cool It Down: A cold or chilled spoon can help alleviate some of the gum soreness.
- Bring Out a Teether: Try giving your little one a silicone or rubber baby teether. Some baby teethers can even be stored in the fridge for a colder temperature that’s more soothing on the gums.
- Water: If your little one is older than 6 – 9 months, try giving them cool water from a sippy cup.
A chilled pacifier may seem like a good option to help soothe your teething baby; however, they should be used with caution. A pacifier that’s damaged from over-chewing can be a choking hazard. Additionally, overusing a pacifier can impact jaw development and tooth alignment.
Breastfeeding and Teething
It’s not uncommon for nursing mothers to face discomfort or hardship when breastfeeding their teething baby. Teething symptoms leave babies uncomfortable, leading them to switch up their position when trying to latch and cause them to find relief by biting.
FAQs
-
How can I tell if my baby is teething?
-
When is normal for babies to start teething?
-
Can my 3-month-old be teething already?
-
How long does teething pain last for babies?
Sources
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/infant-and-toddler-health/in-depth/teething/art-20046378
- https://www.webmd.com/parenting/baby/teething-symptoms-remedies
- https://wicbreastfeeding.fns.usda.gov/breastfeeding-your-teething-baby#:~:text=Your%20baby%20will%20begin%20teething,to%20relieve%20soreness%20by%20biting.
Table of Contents
- When do Babies Start Teething
- Which Baby Teeth Come In First?
- Baby Teeth Eruption Chart
- How many Teeth do Babies have?
- How long does Teething last?
- Signs of Teething In Babies
- Remedies for Soothing Teething Baby
- Breastfeeding and Teething
- FAQs
- Sources

This blog has been reviewed and approved by Dr Robert Lee, a dental professional of 35 years LEARN MORE >

Sign Up
for expert advice and exclusive offers

Sign Up
for expert advice and exclusive offers



